Explore
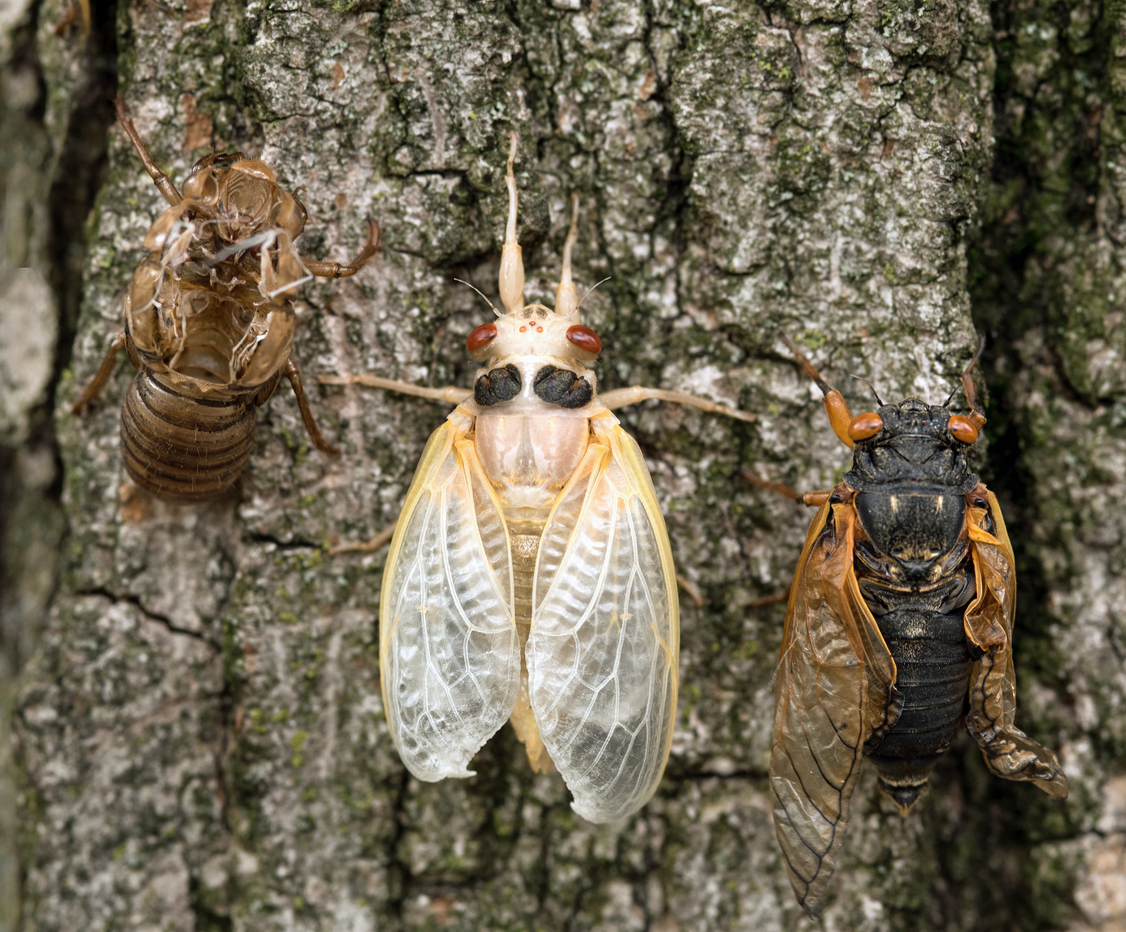

Brood X Cicada Nymph, Adult and Empty Skin
Cicadas
Cicadas make a distinct sound. You probably hear them all the time and don’t realize it’s them, right in your backyard.
Periodical cicadas are only found in eastern North America and are remembered primarily for their prime-numbered life cycles. Because they resurface every 13 or 17 years, Maryland residents are able to witness and enjoy their emergence only during certain years. Farmers, specifically tree farmers may not be as excited about these true bugs. Cicadas feed on fluids from plants above and below the ground. Brood X is the largest brood of 17-year cicadas. These cicadas are not to be confused with annual cicadas, which are green in color.
The emergence of the Brood X cicada is dependent on when the ground temperature reaches 64 degrees, typically in the first or second week of May. When cicadas emerge, they come out in large numbers. This is a survival technique called prey satiation. It allows their predators to feast on them, while still ensuring that a large number of insects remain to breed and keep the species alive. The predators of cicadas include birds, raccoons, opossums, foxes, mice, frogs, toads, certain fish, all kinds of spiders, ants, and wasps. Poultry farmers often feed this protein-rich bug to their chickens.
Cicadas impact the environment in various ways. A massive number of periodical cicadas emerge and can harm young trees because the females lay their eggs in young tree branches. When tree farmers plant trees, they take various measures to protect their crops from pests. Integrated pest management (IPM) is a sustainable approach to managing these pests. It combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools in a way that minimizes economic, health, and environmental risks. For instance, farmers might use netting to protect young trees during spring plantings when cicadas emerge. Pruning or tree trimming can also help manage the damage caused by cicadas. These are examples of mechanical or physical methods of pest control. Cultural forms of IPM include planting native trees in the right place, controlling weeds and cleaning up plant debris. Depriving these pests of what they need to survive prevents further damage from occurring.
As you watch the following video about cicadas and how farmers manage them as pests, think about these questions.
- Where do Brood X cicadas live during the 17 years before they emerge, and how do they get nutrition?
- The Brood X cicada emerged in 2021. When will they emerge again?
- How do cicadas cause damage to trees?